Cladding is a term used to describe the external layer or covering of a building. It is essentially a non-structural layer that is added to the exterior of a building for various purposes such as protection, insulation, and aesthetics. Cladding can be made from a variety of materials and comes in different forms, making it a versatile option for building design.
In recent years, cladding has gained significant attention due to its role in the Grenfell Tower fire tragedy in London. This incident highlighted the importance of understanding the types of cladding used in buildings and the need for proper regulations and safety measures. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of cladding, exploring its types, benefits, materials, installation, maintenance, regulations, safety, aesthetics, and future trends.
Types of Cladding
There are various types of cladding available in the market, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. Some of the most common types of cladding include:
1. Metal Cladding
Metal cladding is a popular choice for commercial and industrial buildings due to its durability and low maintenance requirements. It is typically made from aluminum, steel, or copper and can come in the form of panels, sheets, or shingles. Metal cladding is known for its sleek and modern look, making it a popular choice for contemporary building designs.
Advantages of Metal Cladding
- Durable and long-lasting
- Low maintenance
- Fire-resistant
- Lightweight
- Can be easily recycled
- Provides good thermal insulation
Disadvantages of Metal Cladding
- Expensive compared to other types of cladding
- Prone to denting and scratching
- Can be noisy during heavy rain or hail
- Limited color options
2. Timber Cladding
Timber cladding is a popular choice for residential buildings due to its natural and warm aesthetic. It is made from various types of wood such as cedar, pine, or oak and can come in the form of shingles, boards, or panels. Timber cladding requires regular maintenance to prevent rotting and warping, but it can provide good insulation and soundproofing.
Advantages of Timber Cladding
- Natural and aesthetically pleasing
- Good thermal and acoustic insulation
- Can be easily repaired or replaced
- Environmentally friendly
- Cost-effective compared to other types of cladding
Disadvantages of Timber Cladding
- Requires regular maintenance
- Prone to rotting and warping if not properly maintained
- Can be a fire hazard if not treated with fire-retardant chemicals
- Limited lifespan compared to other types of cladding
3. Brick Cladding
Brick cladding is a traditional and popular choice for both residential and commercial buildings. It involves attaching brick slips or tiles onto the exterior walls of a building, giving it a classic and timeless look. Brick cladding is known for its durability and low maintenance requirements, making it a cost-effective option in the long run.
Advantages of Brick Cladding
- Durable and long-lasting
- Low maintenance
- Provides good thermal insulation
- Fire-resistant
- Can be easily repaired or replaced
- Wide range of colors and textures available
Disadvantages of Brick Cladding
- Heavy and may require additional structural support
- Expensive compared to other types of cladding
- Limited design options
- Can be prone to cracking and water damage if not properly installed
Benefits of Cladding

Cladding offers numerous benefits to buildings, making it a popular choice for architects and designers. Some of the key benefits of cladding include:
- Protection: Cladding acts as a protective layer for buildings, shielding them from harsh weather conditions, UV rays, and pollution.
- Insulation: Certain types of cladding, such as timber and brick, provide good thermal insulation, reducing energy consumption and costs.
- Aesthetics: Cladding can enhance the appearance of a building, giving it a unique and attractive look.
- Durability: Cladding can increase the lifespan of a building by protecting it from wear and tear.
- Low maintenance: Most types of cladding require minimal maintenance, saving time and money in the long run.
Materials Used for Cladding
Cladding can be made from a variety of materials, each with its own unique properties and characteristics. Some of the most commonly used materials for cladding include:
- Metal: As mentioned earlier, metal cladding is typically made from aluminum, steel, or copper.
- Timber: Timber cladding can be made from various types of wood, including cedar, pine, oak, and more.
- Brick: Brick cladding involves attaching brick slips or tiles onto the exterior walls of a building.
- Stone: Stone cladding can be made from natural stone, such as granite, marble, or limestone, or artificial stone, such as fiber cement or concrete.
- Glass: Glass cladding is a modern and sleek option that provides natural light and views while also acting as a protective layer.
- Composite materials: Composite cladding is made from a combination of materials, such as wood and plastic, to provide the benefits of both.
The choice of material for cladding depends on various factors such as budget, location, climate, and design preferences.
Cladding Installation
The installation process for cladding varies depending on the type of cladding and the material used. However, there are some general steps that need to be followed for successful cladding installation:
- Preparation: The first step is to prepare the surface where the cladding will be installed. This involves cleaning the surface and ensuring it is smooth and free from any debris or loose material.
- Waterproofing: If the cladding is being installed on an external wall, it is important to ensure that the wall is waterproofed to prevent water damage.
- Framing: The next step is to install a frame or support structure for the cladding to be attached to. This can be made from wood, metal, or other materials depending on the type of cladding.
- Cutting and fitting: Once the frame is in place, the cladding material needs to be cut and fitted according to the design and measurements.
- Fixing: The cladding is then fixed onto the frame using screws, nails, or adhesives, depending on the type of cladding and material used.
- Finishing: Finally, any gaps or joints are sealed, and finishing touches are added to complete the installation process.
It is important to hire experienced professionals for cladding installation to ensure proper techniques and safety measures are followed.
Maintenance and Cleaning of Cladding
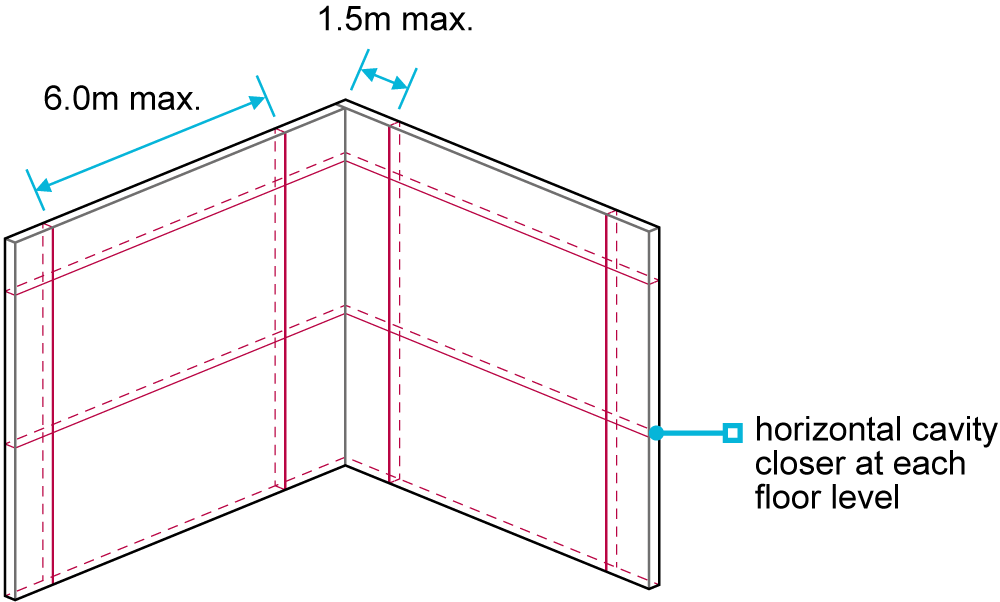
Proper maintenance and cleaning are essential for the longevity and appearance of cladding. The frequency and methods of maintenance and cleaning depend on the type of cladding and material used. Here are some general tips for maintaining and cleaning different types of cladding:
- Metal cladding: Metal cladding requires minimal maintenance, but it is important to regularly check for any scratches or dents and repair them to prevent rusting. It can be cleaned with mild soap and water.
- Timber cladding: Timber cladding requires regular maintenance to prevent rotting and warping. It should be treated with preservatives every few years and cleaned with a mild detergent and water.
- Brick cladding: Brick cladding is low maintenance and can be cleaned with a pressure washer or mild detergent and water.
- Stone cladding: Stone cladding may require occasional sealing to prevent staining and should be cleaned with a mild detergent and water.
- Glass cladding: Glass cladding is easy to clean with a glass cleaner or mild soap and water.
- Composite cladding: Composite cladding requires minimal maintenance and can be cleaned with a mild detergent and water.
It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for maintenance and cleaning to avoid any damage to the cladding.
Cladding Regulations and Standards
In light of the Grenfell Tower fire tragedy, there has been an increased focus on cladding regulations and safety standards. In the UK, the Building Regulations Approved Document B outlines the requirements for external walls and cladding systems. It covers aspects such as fire safety, insulation, and structural stability.
In addition to building regulations, there are also various standards and certifications that cladding materials and systems must adhere to. These include:
- British Standards (BS): BS 8414 is a standard for testing the fire performance of external cladding systems.
- European Standards (EN): EN 13501-1 is a standard for classifying the fire performance of construction products and building elements.
- National Fire Protection Association (NFPA): NFPA 285 is a standard for testing the fire propagation characteristics of exterior non-load-bearing wall assemblies.
It is important for architects, designers, and contractors to stay updated on the latest regulations and standards to ensure the safety and compliance of cladding systems.
Cladding Safety
The Grenfell Tower fire tragedy highlighted the importance of cladding safety and the need for proper regulations and standards. Cladding can pose various safety risks if not installed and maintained correctly. Some of the key safety concerns related to cladding include:
- Fire safety: The type of cladding used and its installation can greatly impact the fire safety of a building. Non-compliant or combustible cladding can lead to rapid fire spread, endangering lives and property.
- Structural stability: Cladding should not compromise the structural stability of a building. Proper installation and maintenance are crucial to prevent any structural issues.
- Water damage: Improperly installed or maintained cladding can allow water to seep into the building, causing damage to the structure and potentially leading to mold growth.
- Falling debris: Cladding that is not securely fixed can pose a risk of falling debris, endangering people and property below.
It is important to follow proper safety measures and regulations when it comes to cladding to ensure the safety of buildings and their occupants.
Cladding Aesthetics
In addition to its functional benefits, cladding also plays a significant role in the aesthetics of a building. It can greatly impact the overall look and feel of a structure, making it an important consideration for architects and designers. Some of the key factors to consider when choosing cladding for aesthetic purposes include:
- Color and texture: The color and texture of cladding can greatly impact the appearance of a building. Different materials offer a wide range of colors and textures to choose from.
- Design and pattern: Cladding can be used to create unique designs and patterns on the exterior of a building, adding visual interest and character.
- Integration with other elements: Cladding should be chosen in a way that complements other elements of the building, such as windows, doors, and roofing.
- Context: The surrounding environment and context should also be considered when choosing cladding to ensure it fits in with the overall aesthetic of the area.
Future Trends in Cladding
As technology and design continue to evolve, so does the world of cladding. Here are some future trends to keep an eye on in the world of cladding:
- Sustainable materials: With a growing focus on sustainability and environmental impact, there is a rise in the use of sustainable materials for cladding, such as recycled plastic, bamboo, and hemp.
- Smart cladding: Advancements in technology have led to the development of smart cladding systems that can monitor and adjust to environmental conditions, providing better insulation and energy efficiency.
- 3D printing: 3D printing technology is being used to create unique and intricate designs for cladding, allowing for more creativity and customization.
- Biophilic design: Biophilic design, which incorporates natural elements into building design, is gaining popularity in the world of cladding. This includes using materials such as living walls, moss, and plants for cladding.
Conclusion
Cladding plays a crucial role in the protection, insulation, and aesthetics of buildings. With a wide range of materials and types available, it offers versatility and flexibility in design. However, proper installation, maintenance, and adherence to regulations and safety standards are essential to ensure the safety and longevity of cladding systems. As technology and design continue to evolve, we can expect to see innovative and sustainable trends in the world of cladding.
Read more blogs : SOFTWARE AND APPS xatpes’s Magical Journey Through the World of Software Development




